Introduction to Networking: How the Internet Works
The goal of this book is to provide a basic understanding of the technical design and architecture of the Internet. The book is aimed at all audiences – even those with absolutely no prior technical experience or math skills. The Internet is an amazingly beautiful design and should be understood by all who use it. There is supporting material for the book at www.net-intro.com.
Introduction to Networking: How the Internet Works
Link Layer
•
Charles R. Severance
This is part of the book "Introduction to Networking" at www.net-intro.com
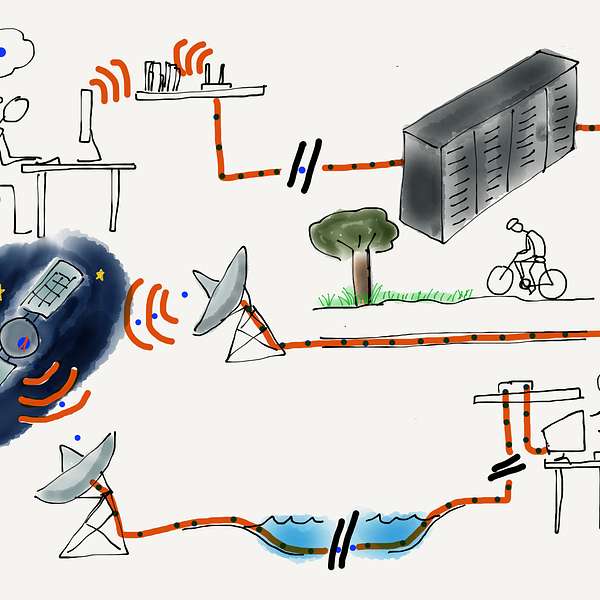
The lowest layer of our Internet Architecture is the Link layer. We call it the "lowest layer" because it is closest to the physical network media. Often the Link layer transmits data using a wire, a fiber optic cable, or a radio signal. A key element of the Link layer is that usually data can only be transmitted part of the way from the source computer to the destination computer. Wired Ethernet, WiFi, and the cellular phone network are examples of link layers that can transmit data about a kilometer. Fiber optic cables, particularly those under the oceans, can transmit data up to thousands of kilometers. Satellite links can also send data over long distances.